Fisher Studios
Rising human tissue artificially might be our greatest wager in changing or restoring operate to components of the physique broken or misplaced by illness and harm. However it doesn’t must be difficult. Generally all you want is a serving to hand.
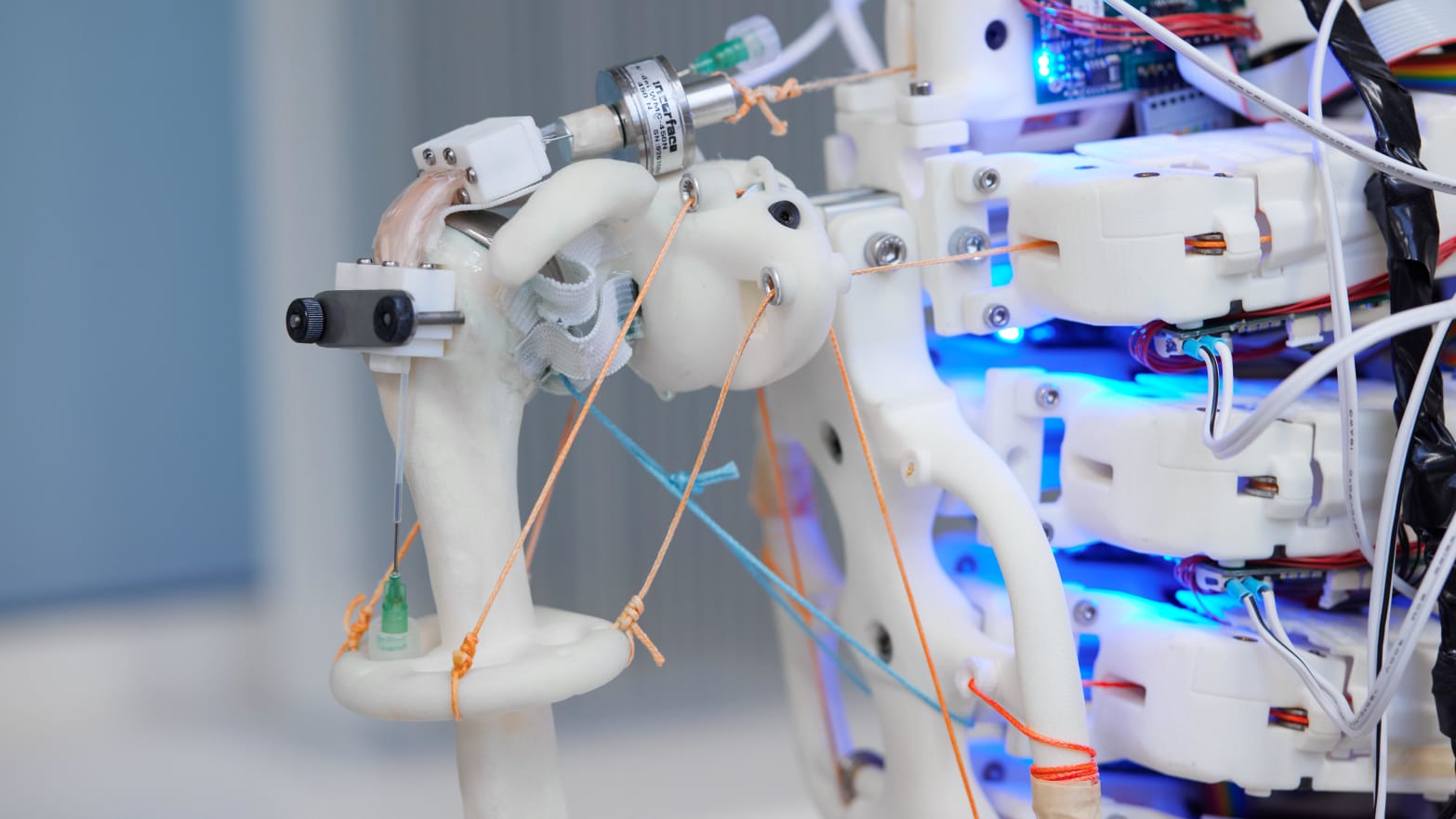
For a workforce of British scientists, that serving to hand is a robotic’s. Researchers at Oxford College, in collaboration with German robotics firm Devanthro, have made a robotic system that eerily appears to be like like one thing straight out of Westworld. In a paper revealed Thursday within the journal Nature, this humanoid robo-shoulder is designed to assist develop human tendons, mushy connective tissues that connect muscle to bone. It could be to deal with these wants and be our ticket to regenerating these tissues extra simply within the lab, serving to thousands and thousands of individuals within the U.S. that suffer from tendon accidents like rotator cuff tears.
Versus artificially rising organs like hearts and brains, finicky tissues like tendons want a bit extra TLC to develop and performance correctly. The difficulties appear to be rooted in stretch and stress, Pierre-Alexis Mouthuy, a bioengineer at Oxford College and lead researcher of the brand new research, instructed The Every day Beast. Tendons, very similar to a rising muscle, want mechanical stimulation both from stretching being uncovered to a weighted load. Exposing tendon cells to those forces influences how these cells mature, how viable they are going to be, and whether or not or not they are going to be capable of operate adequately and even be sturdy sufficient.
However at the moment, scientists don’t have an ideal system to fulfill a tendon’s distinctive mechanical wants. For the final 20 years, bioreactor applied sciences (gadgets that develop tissues) have solely been in a position to stretch tendons in a single path—nothing just like the type of 360-degree paces or heavy lifting we put our tendons by way of day by day.
The appearance of robots, nonetheless, has modified all of that. In pursuit of rising a extra excellent rotator cuff tendon within the lab, Mouthy and his workforce turned to Devanthro.
“[Devanthro] has developed these humanoid robots that use cords to maneuver bone-like constructions in an identical approach to how the human physique would do with muscular tissues and tendons to drag on bone,” he stated. “What we’ve accomplished is modify that system, tailored it to create a type of humanoid bioreactor.”
This humanoid bioreactor does look fairly human—it’s acquired a shoulder joint, a part of an arm, and half of a ribcage with blue lights peeking by way of from all of the hardware stuffed inside. The robotic can almost mimic the total vary of human actions fairly nicely. Mouthuy and his workforce used it to efficiently develop human fibroblasts (the precept cell of connective tissue) in simply two weeks. They haven’t but been in a position to develop a full-sized tendon, however the brand new outcomes pave the trail for researchers to start out making human tendons very quickly, significantly for individuals with rotator cuff accidents.
“Rotator cuff tears are quite common—they are often the reason for trauma, bodily harm, or the results of illness,” stated Mouthuy. “They're very age-dependent, so the older you're, the upper your threat of creating these tears.”
Sometimes, rotator cuff tears are repaired with surgical procedure, however Mouthuy stated a draw back to sewing a tendon again up is that it’s not completely a treatment: It doesn’t enhance a tendon weakening as a result of age or illness.
Mouthuy hopes this new humanoid bioreactor will make it potential to create tendons that not solely substitute torn rotator cuffs (or another tendon harm), but in addition promote higher therapeutic and scale back the necessity for invasive surgical procedure. The robo-shoulder may additionally assist scientists higher perceive the connection between totally different quantities and ranges of mechanical stress and the way these forces affect a cell’s gene expression and finally, what sort of tendon it turns into.
“There’s a necessity for offering higher tissue grafts to the clinic,” he stated. “Not simply higher tissue grafts however biomaterials that will assist help the restore of sentimental tissues. That is what we are attempting to realize with tissue engineering.”